One of the oldest and most important fields of engineering, civil engineering is concerned with the planning, development, and upkeep of the built environment, including buildings, infrastructure, and transportation systems.
It is impossible to undervalue the significance of civil engineering since it is essential to the development of modern civilization. By planning and constructing the infrastructure that supports our everyday life, civil engineers significantly contribute to the development of modern civilization.
According to a report by the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), the United States needs to invest $4.6 trillion by 2025 to meet its infrastructure needs, including roads, bridges, and water supply systems.
Importance of Civil Engineering in Modern Society:
We cannot exaggerate the importance of civil engineering in contemporary society. Civil engineers plan and construct the infrastructure that enables mobility, supports our economy, and ensures that everyone has access to clean electricity and water.
As they are in charge of planning and constructing secure, effective, and long-lasting infrastructure, civil engineers play a crucial role in the growth and development of modern civilization. Modern civilization as we know it would not exist without civil engineering.
Historical Perspective
For thousands of years, civil engineering has been a crucial component of human civilisation. In the past, civil engineers were in charge of planning and constructing buildings like aqueducts, dams, and roadways. When the ancient Egyptians constructed the pyramids around 4000 BCE, they used cutting-edge engineering methods, making it the earliest instance of civil engineering ever recorded.
Civil engineering has developed over time to use increasingly advanced methods and materials. Civil engineers were instrumental in the development of new technologies, such steam engines and steel fabrication, during the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries, which enabled the building of larger and more intricate structures.
Major milestones in the development of Civil Engineering
The Roman Empire was known for its engineering skills, which included the building of water systems, roads, and bridges. Many of the Roman Empire’s historic constructions may still be seen today. The Roman Empire was a significant centre of civil engineering.
Industrial Revolution: The progress of civil engineering underwent a crucial turning point during the Industrial Revolution. Skyscrapers and suspension bridges were made possible by the development of new technologies like steam engines and steel fabrication.
Modern Era: Civil engineering has developed and grown significantly in the modern age. New methods and approaches to civil engineering have been developed as a result of developments in computer technology, materials science, and environmental sustainability. Airports, skyscrapers, and transit networks are just a few of the largest and most complex projects that civil engineers are now in charge of planning and constructing.
Key Areas of Civil Engineering
Civil engineering encompasses a wide range of disciplines and specialties. The following are eleven key areas of civil engineering:
1) Infrastructure:
The term “infrastructure” describes the physical and administrative facilities and structures that underpin modern society, including public buildings, water supply systems, and transportation networks. In order to make sure that infrastructure is secure, effective, and long-lasting, civil engineers are crucial in its planning, construction, and maintenance.
2) Construction:
Buildings, bridges, and other structures and amenities, including roadways, are all examples of construction. From planning to execution, civil engineers are in charge of overseeing all elements of building projects to make sure they are completed without incident, on schedule, and within budget.
3) Design:
The process of developing plans and specifications for buildings and other structures is referred to as design. To create structures that are secure, effective, and long-lasting, civil engineers draw on their knowledge of physics, mathematics, and materials science. They also develop comprehensive designs and models of structures using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
4) Structural Engineering:
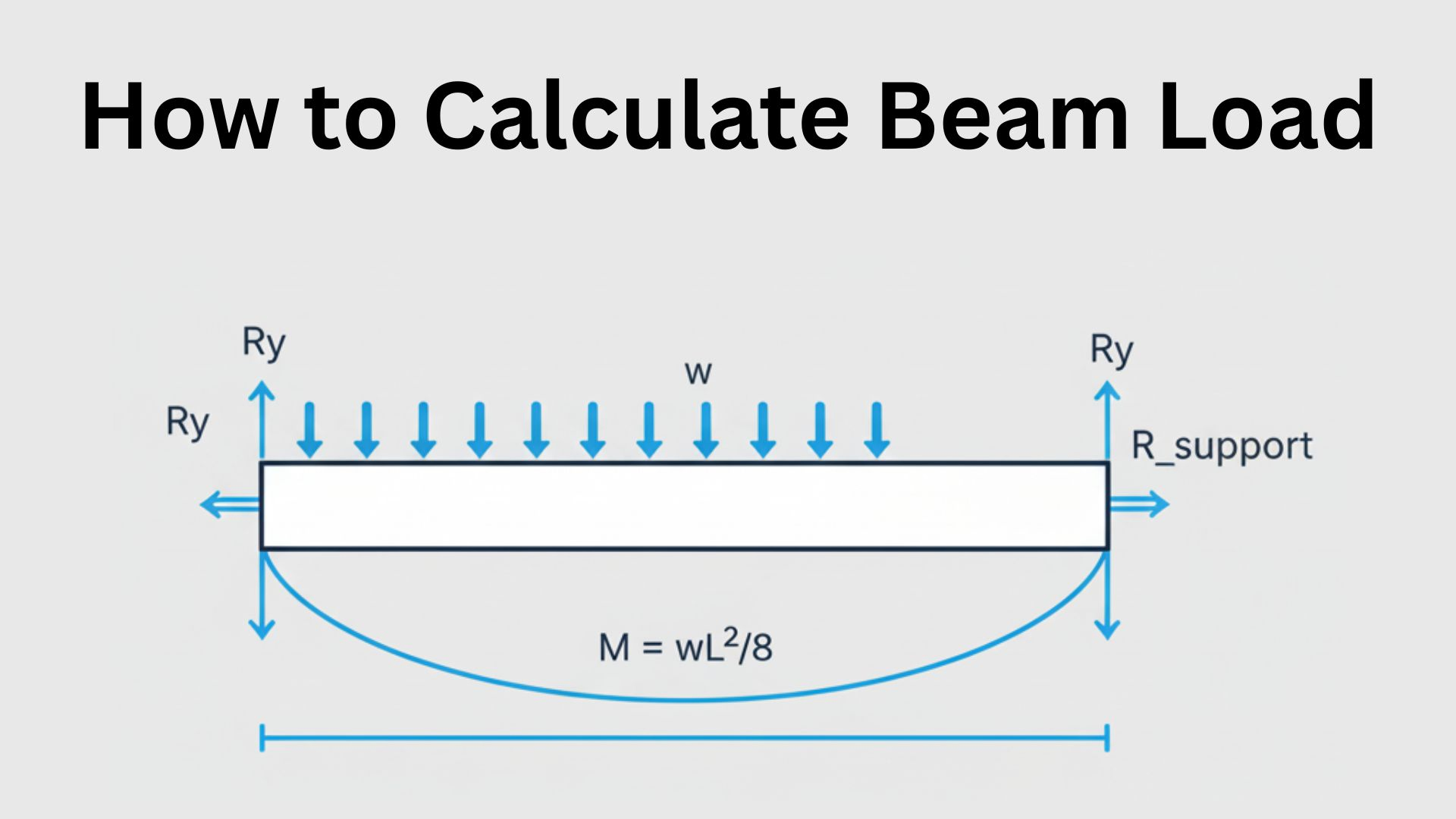
Buildings, bridges, and towers are just a few examples of the structures that structural engineering concentrates on designing and analyzing. In order to make sure that structures are secure, stable, and long-lasting, structural engineers utilize their knowledge of mathematics, physics, and materials science.
5) Environmental Engineering:
Designing and creating solutions for environmental issues including pollution management, water and wastewater treatment, and renewable energy generation are the main areas of interest in environmental engineering. The goal of environmental engineering is to encourage sustainable practices and reduce the negative effects of human activity on the environment.
6) Geotechnical Engineering:
Geotechnical engineering is concerned with how the behaviour of soil and rock impacts the planning and building of buildings. Geotechnical engineers utilize their knowledge of rock and soil physics to guarantee that buildings are constructed securely and safely.
7) Transportation Engineering:
Roads, highways, railroads, and airports are just a few of the transportation systems that are the focus of transportation engineering. Designing safe, effective, and sustainable transportation systems requires the skills of transportation engineers in traffic flow, safety, and environmental impact.
8) Geomatics Engineering:
Maps, aerial photos, and satellite pictures are just a few examples of geographical data that geomatics engineering focuses on gathering, analyzing, and interpreting. In order to create precise and comprehensive maps and other geospatial products, geomatics engineers draw on their knowledge in surveying, mapping, and geographic information systems (GIS).
9) Water Resources Engineering:
Water resources engineering mainly deals with the management and conservation of water resources, including flood prevention, water treatment, and water delivery. To guarantee that water resources are managed in a sustainable and ecologically friendly way, water resources engineers draw on their knowledge of hydraulics, hydrology, and environmental science.
1) Infrastructure
A community or economy’s essential physical and organisational structures and facilities, such as its transportation and communication networks, power plants, and water supply systems, are referred to as infrastructure.
Types of Infrastructure:
There are several types of infrastructure, including:
- Infrastructure for transportation consists of highways, bridges, railroads, airports, and ports.
- Internet and telecommunications networks make up the communication infrastructure.
- Infrastructure for the delivery of energy, such as power plants, pipelines, and distribution systems.
- Infrastructure for the provision of water and wastewater, such as pipelines, sewage treatment facilities, and water supply systems.
Importance of Infrastructure:
Infrastructure is essential for economic growth and development because it makes it possible for people, things, and information to move around with efficiency. It also offers necessities like communication, energy, and access to clean water. Infrastructure systems that are properly created and maintained may raise citizen quality of life and support sustainable growth.
Examples of Infrastructure Projects:
The building of new roadways, the expansion of public transit networks, the creation of renewable energy facilities, and the modernization of water treatment facilities are a few examples of infrastructure projects. Large-scale infrastructure projects must be carefully planned and carried out since they can have a substantial impact on nearby populations and the environment.
2) Construction
Building or assembling structures, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, is referred to as construction. To generate a final product, the building process uses a range of materials, equipment, and procedures.
Importance of Construction:
Construction facilitates the construction of the physical infrastructure required for economic growth and development, making it a crucial component of civil engineering. Well-built buildings may enhance the safety and effectiveness of transportation networks and other infrastructure amenities while also enhancing the quality of life for residents.
Phases of Construction:
There are often multiple stages to the construction process, including:
- Planning and Design: During this stage, engineers and architects create the project’s plans and requirements.
- Site preparation include cleaning the site and getting it ready for building.
- Pouring the foundation and creating the building’s primary structure are included in the foundation and structural steps.
- Installation of systems: This includes setting up mechanical and technical systems including HVAC, plumbing, and electrical.
- Finishing: This stage entails providing the project with the final touches, such as paint, flooring, and fittings.
Examples of Construction Projects:
Examples of construction projects include building new structures, enlarging or renovating existing structures, building roads and bridges, and creating infrastructural facilities like water treatment and electricity production plants. Large-scale building projects need to be carefully planned and managed since they may have a big influence on the economy, the environment, and society.
Also Read – Mastering Construction Cost Estimation: Methods, Tools, and Best Practices for Accurate Project Budgeting
3) Design
Design is the process of creating plans and specifications for a project, such as a building or infrastructure facility. The design process involves identifying the requirements and constraints of the project, developing a concept or idea, and creating detailed plans and specifications that guide the construction process.
Importance of Design:
Design is a critical part of civil engineering, as it ensures that the infrastructure and buildings constructed are safe, efficient, and functional. Well-designed structures and facilities can improve the quality of life for citizens and enhance economic growth and development.
Principles of Design:
The principles of design include:
- Functionality: The design should meet the functional requirements of the project.
- Safety: The design should ensure the safety of the users and the surrounding environment.
- Sustainability: The design should be sustainable and minimize the environmental impact of the project.
- Aesthetics: The design should be visually appealing and contribute to the beauty of the surrounding area.
- Cost-effectiveness: The design should be cost-effective and provide value for money.
Examples of Design Projects:
Examples of design projects include the design of buildings, bridges, and roads, as well as the development of infrastructure facilities, such as water treatment plants and power generation facilities. Civil engineers use a variety of tools and techniques to create detailed plans and specifications, such as computer-aided design (CAD) software and 3D modeling tools.
4) Structural Engineering:
Structural engineering is a subfield of civil engineering that deals with the design and analysis of structures, such as buildings, bridges, and towers. Structural engineers ensure that structures are safe, reliable, and resistant to natural disasters such as earthquakes and hurricanes.
Importance of Structural Engineering:
Structural engineering is a critical field in civil engineering, as it ensures that structures are designed to withstand the forces that they will encounter during their lifetime. By using advanced techniques and materials, structural engineers can create structures that are stronger, lighter, and more durable, which can improve safety and reduce construction costs.
Examples of Structural Engineering:
Examples of structural engineering projects include the design of skyscrapers, stadiums, and bridges. Structural engineers use computer simulations, mathematical models, and physical testing to ensure that structures can withstand the loads and stresses that they will experience over time. In recent years, structural engineers have been using new materials, such as carbon fiber and high-strength concrete, to create lighter and more durable structures.
5) Environmental Engineering:
Environmental engineering is a subfield of civil engineering that deals with the application of science and engineering principles to protect and improve the environment. Environmental engineers work to identify and address environmental problems, such as air and water pollution, and design systems to prevent or mitigate these problems.
Importance of Environmental Engineering:
Environmental engineering is important because it addresses many of the environmental issues facing our planet, including pollution and climate change. Environmental engineers use their knowledge of biology, chemistry, and physics to design solutions that protect and improve the environment, while also meeting the needs of society.
Examples of Environmental Engineering:
Examples of environmental engineering projects include the design and implementation of wastewater treatment systems, the development of air pollution control technologies, and the design of systems to manage hazardous waste. Environmental engineers also work to address the impact of human activities on the environment, such as designing sustainable land use practices and developing renewable energy systems. With the growing concern for climate change, environmental engineers play a critical role in developing solutions that can mitigate the impact of human activities on the environment.
6) Geotechnical Engineering:
Geotechnical engineering is a subfield of civil engineering that focuses on the behavior and properties of soil and rock, and how they affect the design and construction of structures. Geotechnical engineers use their knowledge of geology, soil mechanics, and rock mechanics to ensure that structures are safe and stable, and to minimize the risks associated with natural disasters such as landslides and earthquakes.
Importance of Geotechnical Engineering:
Geotechnical engineering is important because the properties of soil and rock play a critical role in the design and construction of civil infrastructure. By understanding the behavior of soil and rock, geotechnical engineers can ensure that structures are safe, stable, and durable, and can minimize the risks associated with natural disasters.
Examples of Geotechnical Engineering:
Examples of geotechnical engineering projects include the design of foundations for buildings and bridges, the stabilization of slopes and embankments, and the design of underground tunnels and excavations. Geotechnical engineers use a variety of tools and techniques to investigate the properties of soil and rock, such as drilling, sampling, and laboratory testing. With the growing demand for infrastructure around the world, geotechnical engineering plays a critical role in ensuring that structures are safe, reliable, and sustainable.
7) Transportation Engineering:
Transportation engineering is a subfield of civil engineering that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of transportation systems, including roads, bridges, highways, airports, and railways. Transportation engineers work to ensure that these systems are safe, efficient, and sustainable, and meet the needs of society.
Importance of Transportation Engineering:
Transportation engineering is important because transportation systems are critical to the functioning of modern society. They facilitate the movement of goods and people, and are essential to economic development and social well-being. Transportation engineers use their knowledge of traffic flow, safety, and sustainability to design and improve transportation systems, and to ensure that they meet the needs of society.
Examples of Transportation Engineering:
Examples of transportation engineering projects include the design of highways and interchanges, the development of intelligent transportation systems, and the planning and design of public transit systems. Transportation engineers also work to improve the safety and sustainability of transportation systems, such as designing pedestrian and bicycle facilities, and promoting the use of electric vehicles and alternative fuels. With the increasing demand for transportation infrastructure around the world, transportation engineering plays a critical role in ensuring that these systems are safe, efficient, and sustainable.
8) Geomatics Engineering:
Geomatics engineering is a subfield of civil engineering that deals with the acquisition, processing, analysis, and management of spatial data. This includes surveying, remote sensing, geographic information systems (GIS), and global positioning systems (GPS). Geomatics engineers use their knowledge of these technologies to support a wide range of civil engineering projects, from infrastructure development to environmental management.
Importance of Geomatics Engineering:
Geomatics engineering is important because spatial data is critical to many civil engineering projects, including the design and construction of infrastructure, the management of natural resources, and the assessment of environmental impacts. Geomatics engineers use their expertise in surveying, remote sensing, and GIS to collect and analyze spatial data, and to provide insights and solutions to complex engineering problems.
Examples of Geomatics Engineering:
Examples of geomatics engineering projects include the design and construction of highways and transportation systems, the assessment of natural hazards such as floods and landslides, and the management of water resources and environmental impacts. Geomatics engineers also play a critical role in supporting disaster management and emergency response efforts, by providing accurate and up-to-date spatial data to decision-makers. With the increasing importance of spatial data in civil engineering, geomatics engineering is becoming an increasingly vital subfield in the industry.
9) Water Resources Engineering:
Water resources engineering is a subfield of civil engineering that deals with the design, construction, and management of water supply and distribution systems, wastewater treatment and disposal systems, and water management systems such as dams, levees, and irrigation networks. Water resources engineers work to ensure that water resources are used in a sustainable manner, and that communities have access to safe and reliable water supplies.
Importance of Water Resources Engineering:
Water resources engineering is important because water is a finite resource that is essential to human survival and economic development. Water resources engineers use their expertise to ensure that water resources are used efficiently and sustainably, and that communities have access to safe and reliable water supplies. They also play a critical role in managing the risks associated with flooding and other water-related hazards, and in protecting the natural environment.
Examples of Water Resources Engineering:
Examples of water resources engineering projects include the design and construction of water treatment plants, the management of water distribution networks, the design and construction of flood control systems such as dams and levees, and the planning and design of irrigation systems for agriculture. Water resources engineers also work to promote sustainable water use practices, such as the use of low-flow fixtures and water reuse systems, and to protect natural ecosystems and habitats that rely on water resources. With the increasing demand for water resources around the world, water resources engineering is becoming an increasingly vital subfield in industry.
Future of Civil Engineering
Emerging Technologies:
The field of civil engineering is constantly evolving, with emerging technologies that are revolutionizing the way projects are designed, constructed, and managed. These technologies include Building Information Modeling (BIM), 3D printing, drones, and robotics, among others. BIM, for example, allows for the creation of virtual models of buildings and infrastructure projects, which can be used to identify potential problems and optimize designs. Drones and robotics are being used for site inspections and monitoring, while 3D printing is being explored as a way to rapidly construct buildings and other structures.
Advancements in Sustainability:
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important aspect of civil engineering, as communities and governments around the world strive to reduce their carbon footprint and promote sustainable development. Advancements in sustainable materials, such as bio-based materials and recycled aggregates, are enabling engineers to design and construct more eco-friendly buildings and infrastructure projects. Green infrastructure, such as green roofs and rain gardens, is also being integrated into projects to reduce stormwater runoff and improve air quality.
Importance of Collaboration:
Collaboration is critical to the future of civil engineering, as projects become more complex and require expertise from multiple disciplines. Civil engineers will need to work closely with architects, urban planners, environmental scientists, and other professionals to design and construct sustainable and resilient infrastructure that meets the needs of communities. Collaborative tools, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, are also becoming more important for project visualization and communication.
In conclusion, the future of civil engineering is bright, with emerging technologies and advancements in sustainability enabling engineers to design and construct more innovative and resilient infrastructure. Collaboration among professionals from multiple disciplines will be critical to success in the coming years.
Conclusion
In conclusion, civil engineering plays a vital role in modern society, and its importance is only increasing with time. From infrastructure to sustainability, design to construction, civil engineering covers a broad spectrum of disciplines that impact our daily lives. The field of civil engineering is constantly evolving, with emerging technologies and advancements in sustainability shaping the future of the industry. Collaboration among professionals from multiple disciplines will be essential to designing and constructing innovative and resilient infrastructure that meets the needs of communities in the years to come. As we look to the future of civil engineering, it is clear that the field will continue to be at the forefront of driving positive change in our world.