You can easily and quickly Calculate Construction Cost of building your dream home by using our construction cost calculator. Also, we explained how to calculate the cost with the construction thumb rule.
Our online build cost calculator offers accurate and dependable figures by using construction thumb rules to calculate the cost of construction. You can easily estimate your construction project cost with our simple and user-friendly interface.
Our online building cost calculator is the best tool for calculating the construction cost for homeowners, contractors and developers.
Calculate Construction Cost
If you are in a hurry then use our free online Construction Cost calculator to calculate the cost of construction of a house.
If not then read the article.
How do I calculate the cost of materials to build a house?
There are many methods to calculate the cost of materials required to build a house. Here is a step-by-step general process to calculate the cost of materials.
Step 1 – Create a Detailed Construction Plan: First you have to create a detailed construction plan of a house. The detailed plan should include floor plans, architectural drawings and a list of materials required to build a house.
Step 2 – Calculate Quantity of Materials: Use a plan of your house and its details to calculate the quantity of materials required for each part of a building. This includes materials required for building foundation, walls, roof. Also, for flooring, windows, doors. The quantity of plumbing and electrical fittings and any other specific features also be calculated with the help of your plan.
Step 3 – Research Material Cost: Make a list of all the materials you need. Then Find local suppliers to know about the material quality and the pricing. Make a list of prices from each store. Take the best deal by considering material quality, quantity. Purchase in bulk to get a huge discount.
Step 4 – Calculate Material Costs: Multiply the total quantity required with each unit price to get the total cost of that material. Add all material cost to get a total material price.
Step 5 – Construction Wastage: Add 10% to 15% cost in total cost by considering the wastage. 10% to 15% cost is a thumb general rule in construction industry.
Step 6 – Material Delivery and Handling Charges: It includes transportation fees, rent of a crane, or labor costs for handling of the material.
The cost of material depends on location, market condition, project requirements etc. Update the cost estimate regularly to maintain accuracy.
Also Read – How to Minimize Wastage in Construction and save money?
How much material is required for a 1,000 sq ft house?
In India quantity of material requirements for construction of 1,000 sq ft house. It depends on Type of construction, design of a house, finishing materials used and many other reasons.
Here is a general quantity requires to build a 1,000 sq ft House in India. The figures given are not accurate. All the figures are approximate.
Cement: 400-450 bags of cement each having 50 kg may be required for the foundation, walls, and plastering
Sand: 600-650 cubic feet of sand is required for masonry work, plastering, and concreting.
Aggregate: Approximately 1,200-1,300 cubic feet of aggregate (coarse and fine) is commonly required. Sand is known as fine aggregate. If the particles of aggregate are larger than 4.75mm then the aggregate is called coarse aggregate. And if the particles of aggregate are smaller than 4.75mm then the aggregate is called as fine aggregate.
Bricks: 7,000 to 10,000 standard size bricks needed for a 1,000 sq ft house. The no of bricks depends on the size of bricks.
Steel: 5 to 6 metric tons of steel bars are used for a 1,000 sq ft house. The steel reinforcement quantity depends upon the structural design of a house.
Tiles: 900-1,100 square feet of tiles are required for a 1,000 sq ft house. The number of tiles required depends on the size, design, and area to be tiled.
Paint: 50-60 liters of paint for the interior and exterior of a 1,000 sq ft house. The paint quantity depends on the number of coats, surface area, and paint type etc.
Other materials: Other materials are based on your plan and your requirements. These materials include doors, windows, electrical fittings, plumbing, roofing, and insulation materials.
Note – These estimates are approximate. Actual numbers can vary based on the design, construction techniques, and regional factors. Consult with your architects, contractors or engineers for accurate estimates based on your house design and construction plans.
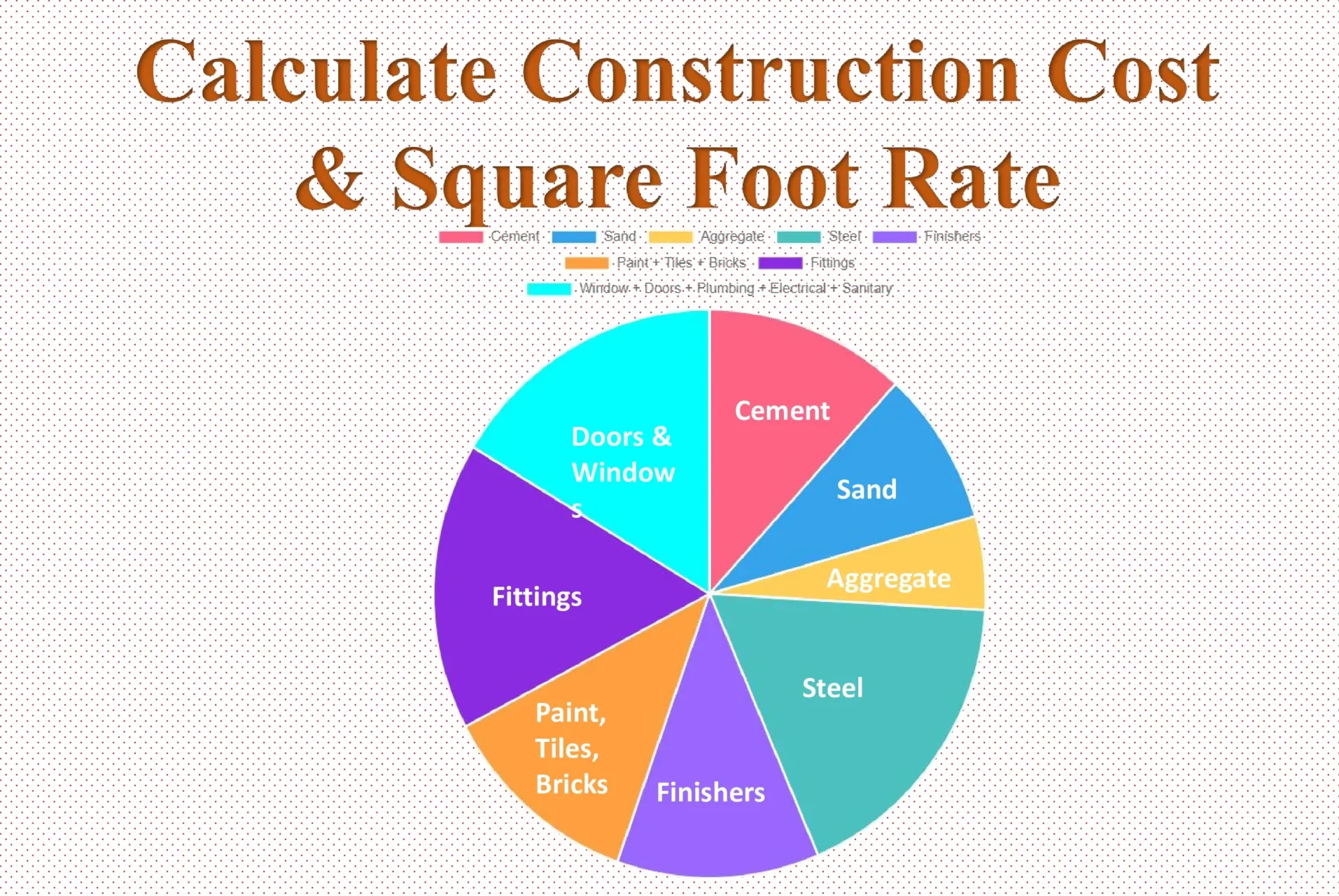
Thumb rule for Material Costs
The approximate cost on various work or material is as below as per thumb rule. (source)
| Sr. No. | Material and Work | Percentage |
| 1 | Cement | 16.4% |
| 2 | Sand | 12.3% |
| 3 | Aggregate | 7.4% |
| 4 | Steel | 24.6% |
| 5 | Finishers (Paint = 4.1% + Tiles = 8.0% + Bricks = 4.4%) | 16.5% |
| 6 | Fittings (Window = 3%, Doors = 3.4%, Plumbing = 5.5%, Eletrical = 6.8%, Sanitary = 4.1%) | 22.8% |
How do you calculate square foot rate?
If you are in hurry then please use this calculator to calculate square foot rate of a house. If not then read the article.
To calculate the square foot rate of a property, you need to divide the price of the property by its total area in square feet.
The formula is:
Square Foot Rate = Property Price / Property Area (in square feet)
Here are the steps to calculate the square foot rate:
- Obtain the price of the property.
- Determine the total area of the property in square feet. This can typically be found in property documents or provided by a real estate agent.
- Divide the property price by the property area to calculate the square foot rate.
For example, if a property is priced at $500,000 and has a total area of 2,500 square feet, the square foot rate would be:
Square Foot Rate = 500,000 / 2,500 square feet
= 200 per square foot
Therefore, the square foot rate for the property would be $200 per square foot. This rate can be used for comparison purposes when evaluating other properties or assessing the value of the investment.
FAQ’s
1) What is RCC in construction?
RCC in construction stands for Reinforced Cement Concrete. It is a composite material widely used in construction for structural components such as beams, columns, slabs, and foundations. RCC combines the strength of concrete and the tensile strength of steel reinforcement to create a sturdy and durable construction material.
2) What is PCC work?
PCC work refers to Plain Cement Concrete. It is a mixture of cement, fine aggregates (such as sand), and coarse aggregates (such as gravel or crushed stone) in a specific ratio. PCC is primarily used as a base or sub-base layer in construction to provide a level surface for further construction activities. It is commonly used for flooring, leveling beds for footing, and as a protective layer over the foundations.
3) Which is better, PCC or RCC?
| Factor | PCC | RCC |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | PCC is mainly used as a base or protective layer | RCC is used for structural elements that require both strength and durability. |
| Composition | PCC is made of cement, fine aggregates, and coarse aggregates. | RCC includes these materials with steel reinforcement. |
| Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity | Lower strength and load-bearing capacity | Higher strength and load-bearing capacity due to steel reinforcement |
| Applications | PCC is primarily used for non-structural elements, such as flooring and leveling | RCC is suitable for constructing beams, columns, slabs, and other load-bearing components. |
4) What are the 3 types of foundations?
The three types of foundations commonly used in construction are:
- Strip Foundation: This type of foundation is a continuous strip of concrete or masonry that supports the load of a wall or a line of columns. It is shallow in depth and spreads the load over a larger area.
- Raft Foundation: Also known as a mat foundation, it is a large concrete slab that covers the entire area beneath a structure. Raft foundations are used when the soil has a low bearing capacity or when the loads on the structure are heavy and need to be distributed over a wider area.
- Pile Foundation: Pile foundations are used when the soil is weak or unstable. They involve driving vertical columns, called piles, deep into the ground to transfer the load of the structure to more stable soil or rock layers below. Pile foundations are commonly used in tall buildings, bridges, and structures located in areas with soft or waterlogged soil.